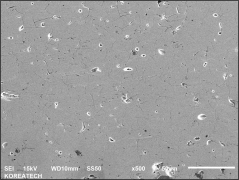
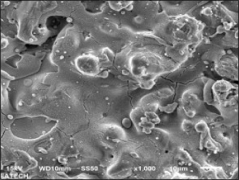
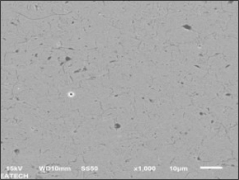
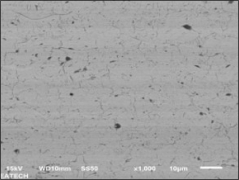
Atmospheric plasma spraying (APS)
Atmospheric plasma spraying may be the most widely used of all thermal spraying processes, as there are almost no limitations in terms of material, size, and shape for both sprayable materials and substrates. The difference between plasma spraying technology and other techniques lies in its applicability and ability to handle a variety of materials, including metals and refractory materials at atmospheric pressure.
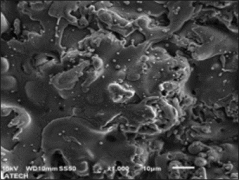
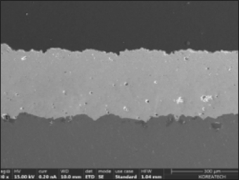
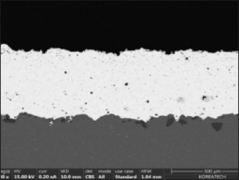
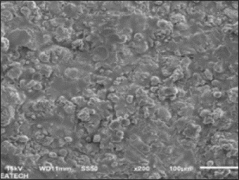
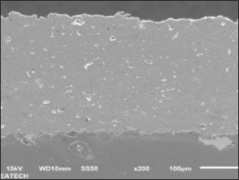
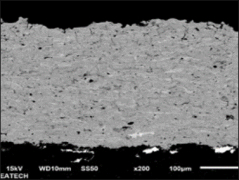
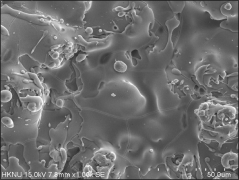
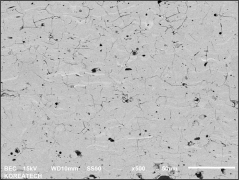
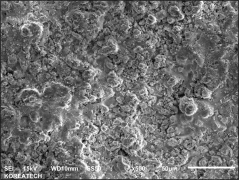
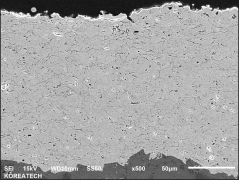
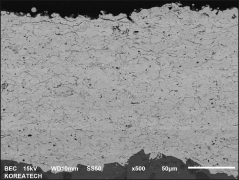
Plasma spraying is a thermal spraying process that uses high-energy heat sources (over 10000 ℃) to melt and accelerate fine particles onto a prepared surface. When impacted, these molten particles (or droplets) cool and immediately solidify by transferring heat to the underlying substrate, thus forming a coating composed of multiple thin layers of droplets through accumulation. For many years, thermal spraying technology has been used to deposit layered coatings for various purposes such as wear resistance, thermal barrier, biocompatibility, and bioactivity.